Forex
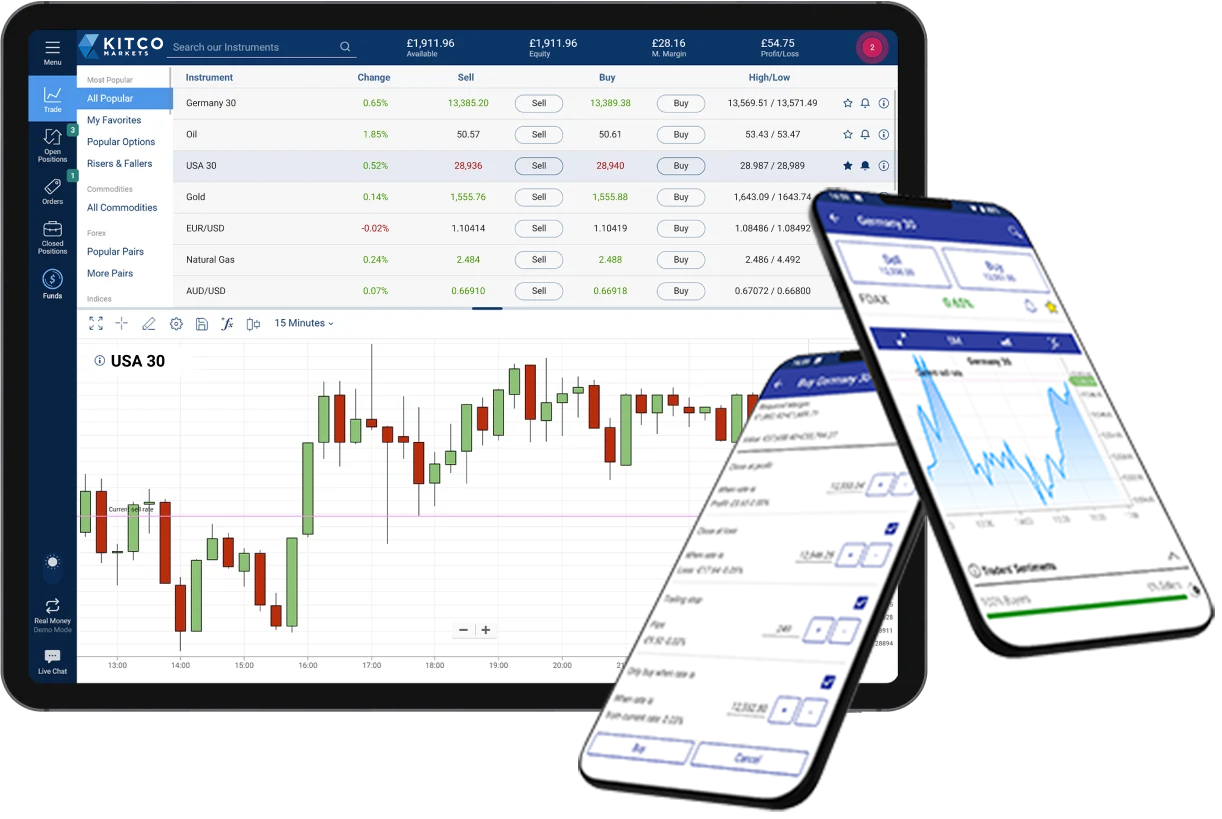
Trade the most popular forex pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD and EUR/GBP with Kitco.

Use our trading tools to limit losses and lock in profits!
If you would like to open a Live Account or practice with a FREE Demo account please click below and get started today!
Forex Spread
How does Forex Trading work?

- Spot Forex Market – The physical exchange of a currency pair, taking place on the spot date (generally, this refers to the day of the trade plus 2 days – “T+2”).
- Forward Forex Market – An Over the Counter (OTC) contract to Buy or Sell a set amount of a currency at a certain price at a future date.
- Forex Futures Market – A forex futures contract is an exchange-traded contract to Buy or Sell a specified amount of a given currency at a predetermined price on a set date in the future.
- Central banks – The world’s money supply is determined by central banks. If a central bank increases the money supply, the currency will likely drop. Generally, central banks also control interest rate levels, which is critical to the strength or weakness of a currency.
- Economic data – Reports on the state of the economy serve as an important indicator of the currency’s strength. Major economic data includes: unemployment rates, inflation rates and trade balances.
- Interest rates – Volatile currency moves tend to occur when a country’s central bank makes an unexpected move in interest rates. For example: if a central bank decides to unexpectedly cut interest rates, the currency will normally lead to a significant drop in value (as the market responds to the sudden change in monetary policy).
- Pip – Generally the lowest increment in which a currency pair is priced.
- Spread – The difference between the Buy/Sell (Bid/Ask) price for a currency pair.
- Leverage – Allows you to trade higher amounts with less capital. A leverage of 1:50 means you would need $200 to place a $10,000 trade.
- Exchange Rate – The value of a base currency against a quoted currency.
- Bid – The price at which the trader is willing to buy the currency pair.
- Ask – The price at which the trader is willing to sell the currency pair.
